As a nutritionist, I have always been fascinated by the Mediterranean diet. It is not only a way of eating but a lifestyle that has been shown to be beneficial for overall health. The Mediterranean diet is based on the traditional eating patterns of people living in countries surrounding the Mediterranean Sea, such as Greece, Italy, and Spain. In this article, I will explain the basics of the Mediterranean diet, its benefits, and the top 10 foods you need to try to transform your health.
Introduction to the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is a way of eating that emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. It also includes fish, seafood, and poultry, while red meat and sweets are limited. Olive oil is the primary source of fat in the Mediterranean diet, and moderate amounts of dairy products, such as cheese and yogurt, are also consumed.
The Mediterranean diet is not only about the foods you eat but also about how you eat. It emphasizes the importance of sharing meals with family and friends, enjoying food in moderation, and being physically active. The Mediterranean diet has been shown to be effective in reducing the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Benefits of the Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet has numerous health benefits due to its nutrient-dense, whole-foods-based approach. The diet is rich in antioxidants, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, which all have positive effects on health. Studies have shown that following the Mediterranean diet can reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke, improve brain function, and decrease the risk of certain types of cancer.
It’s also been associated with a longer lifespan and better overall health. So, what’s the secret? The Mediterranean diet is rich in plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, which are all packed with nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and minerals. It’s also low in processed foods, red meat, and added sugars, which are all linked to chronic illnesses.
In addition to its nutrient density, the Mediterranean diet is also rich in healthy fats like olive oil, fatty fish, and nuts. These fats are important for brain health, heart health, and overall wellbeing. The Mediterranean diet also emphasizes moderate alcohol consumption, particularly red wine, which is rich in antioxidants that can reduce inflammation and improve heart health.
Mediterranean Diet vs Other Diets
The Mediterranean diet has been compared to other popular diets, such as the low-fat diet and the low-carb diet. While all diets have their benefits and drawbacks, studies have shown that the Mediterranean diet is more effective in improving overall health.
Compared to the low-fat diet, which restricts all types of fat, the Mediterranean diet emphasizes healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil and nuts, which have been shown to improve heart health. The Mediterranean diet also includes more whole grains, fruits, and vegetables than the low-fat diet.
Compared to the low-carb diet, which restricts carbohydrates, the Mediterranean diet includes whole grains, which provide important nutrients and fiber. The Mediterranean diet is also more sustainable and easier to follow long-term than the low-carb diet.
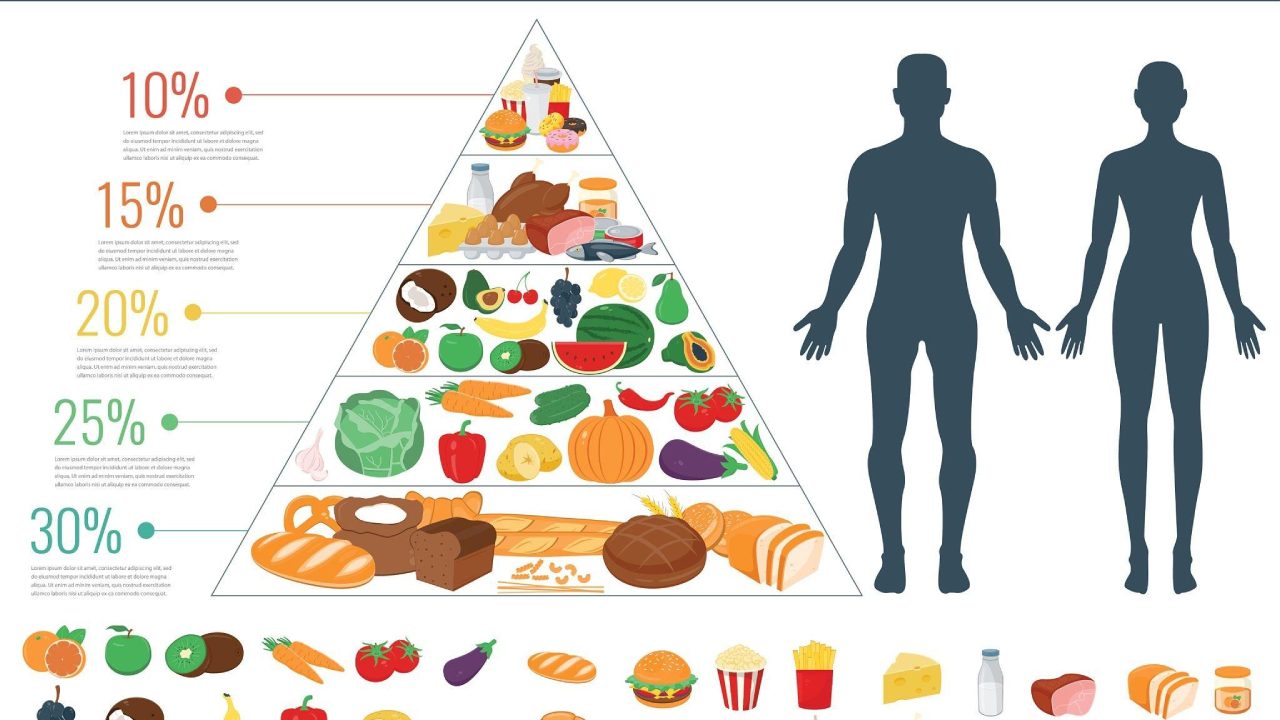
Mediterranean diet food pyramid
The Mediterranean diet is often represented by a food pyramid that highlights the different food groups and how much of each should be consumed. The base of the pyramid is made up of plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, which should be consumed in abundance.
The next level includes healthy fats like olive oil, fatty fish, and nuts. These should be consumed in moderation. The next level includes lean proteins like poultry, eggs, and dairy products, which should also be consumed in moderation. Finally, at the top of the pyramid are sweets and red meat, which should be consumed sparingly.
Top 10 Foods to Try on the Mediterranean Diet
- Olive Oil: Olive oil is the primary source of fat in the Mediterranean diet. It is rich in healthy monounsaturated fats, which have been shown to reduce inflammation and improve heart health. Use olive oil as a salad dressing or for cooking.
- Nuts and Seeds: Nuts and seeds are another source of healthy fats in the Mediterranean diet. They are also rich in protein, fiber, and important nutrients. Try almonds, walnuts, pistachios, sunflower seeds, or pumpkin seeds.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Fruits and vegetables are the foundation of the Mediterranean diet. They are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and have been shown to reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Try to eat a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables every day.
- Whole Grains: Whole grains are an important source of fiber and nutrients in the Mediterranean diet. Try whole-grain bread, pasta, couscous, or brown rice.
- Fish and Seafood: Fish and seafood are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have been shown to improve heart health. Try salmon, tuna, sardines, mackerel, or shrimp.
- Dairy Products: Dairy products are consumed in moderation in the Mediterranean diet. They are a source of protein and important nutrients. Try Greek yogurt, feta cheese, or mozzarella cheese.
- Poultry and Eggs: Poultry and eggs are consumed in moderation in the Mediterranean diet. They are a source of protein and important nutrients. Try chicken, turkey, or eggs.
- Red Meat: Red meat is limited in the Mediterranean diet. When consumed, it is usually in small portions. Try lean cuts of beef, lamb, or pork.
- Herbs and Spices: Herbs and spices are used to flavor food in the Mediterranean diet instead of salt. They provide important antioxidants and have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. Try basil, oregano, thyme, or rosemary.
- Legumes: Legumes, such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas, are an important source of protein and fiber in the Mediterranean diet. They have been shown to reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Try adding them to soups, salads, or stews.
Mediterranean Diet Recipes
Here are three easy and delicious Mediterranean diet recipes to try:
- Greek Salad: Combine chopped romaine lettuce, cherry tomatoes, cucumber, red onion, and feta cheese in a bowl. Drizzle with olive oil and red wine vinegar.
- Baked Salmon: Place a salmon fillet in a baking dish. Top with sliced lemon, garlic, and dill. Drizzle with olive oil and bake in the oven at 375°F for 15-20 minutes.
- Mediterranean Quinoa Bowl: Cook quinoa according to package instructions. Top with chopped cucumber, cherry tomatoes, kalamata olives, feta cheese, and a drizzle of olive oil.
Tips for following the Mediterranean diet
Here are some tips for incorporating the Mediterranean diet into your lifestyle:
- Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts.
- Use healthy fats like olive oil, avocado, and nuts instead of butter or margarine.
- Choose lean proteins like chicken, turkey, and fish instead of red meat.
- Limit processed foods, sweets, and added sugars.
- Enjoy moderate amounts of red wine with meals.
- Experiment with new flavors and spices like basil, oregano, and garlic.
- Plan ahead and prep meals and snacks in advance.
Mediterranean diet meal plan ideas
If you’re interested in incorporating the Mediterranean diet into your lifestyle, here are some meal plan ideas to get you started:
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt parfait with fresh berries, nuts, and honey
- Lunch: Grilled chicken or fish with a Greek salad and whole-grain pita bread
- Dinner: Whole-grain pasta with tomato sauce, roasted veggies, and a sprinkle of Parmesan cheese
- Snack: Fresh fruit or a handful of almonds
- Dessert: Fruit sorbet or a small piece of dark chocolate
Frequently Asked Questions About Mediterranean Diet Foods
What is the Mediterranean diet?
The Mediterranean diet is a way of eating that is based on the traditional diets of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, such as Greece, Italy, and Spain. It is characterized by an emphasis on whole foods, plant-based foods, healthy fats, and moderate consumption of fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy, and limited intake of red meat and processed foods.
What are the key foods in the Mediterranean diet?
The Mediterranean diet is rich in a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, olive oil, fish, seafood, poultry, eggs, dairy (in moderation), and herbs and spices. These foods are typically consumed in balanced proportions, making the Mediterranean diet a nutrient-rich and diverse eating pattern.
What fruits and vegetables are commonly consumed in the Mediterranean diet?
The Mediterranean diet encourages the consumption of a wide variety of fruits and vegetables. Commonly consumed fruits include apples, oranges, grapes, strawberries, figs, and pomegranates. Popular vegetables in the Mediterranean diet include tomatoes, cucumbers, spinach, kale, eggplants, bell peppers, and zucchini.
What whole grains are included in the Mediterranean diet?
The Mediterranean diet emphasizes the consumption of whole grains, which are minimally processed and retain their natural fiber and nutrient content. Examples of whole grains commonly consumed in the Mediterranean diet include whole wheat, brown rice, quinoa, bulgur, couscous, and oats.
What are healthy fats in the Mediterranean diet?
Healthy fats are a key component of the Mediterranean diet and are typically obtained from plant-based sources. Olive oil is a primary source of healthy fats in the Mediterranean diet, along with nuts and seeds such as almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds. Avocados and fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are also good sources of healthy fats in the Mediterranean diet.
How much fish and seafood should I eat in the Mediterranean diet?
The Mediterranean diet recommends consuming fish and seafood at least twice a week. Fish and seafood are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which are heart-healthy fats that can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Is red meat allowed in the Mediterranean diet?
While the Mediterranean diet does not exclude red meat entirely, it is typically consumed in limited amounts. The emphasis is on lean protein sources such as fish, poultry, legumes, and nuts. Red meat is often consumed in small portions and as an occasional treat rather than a staple food in the Mediterranean diet.
Are dairy products allowed in the Mediterranean diet?
Dairy products are included in the Mediterranean diet, but typically in moderation. Examples of dairy products commonly consumed in the Mediterranean diet include yogurt, cheese, and occasionally milk. However, the emphasis is on choosing low-fat or reduced-fat options and consuming them in moderate amounts.
Can I have sweets and desserts in the Mediterranean diet?
The Mediterranean diet does allow for occasional consumption of sweets and desserts, but in limited quantities. The emphasis is on choosing natural sources of sweetness such as fresh fruits, dried fruits, and honey, rather than processed or refined sugars. Sweets and desserts are typically consumed in small portions and as part of an overall balanced diet.
Conclusion
The Mediterranean diet is a way of eating that emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. It also includes fish, seafood, and poultry, while red meat and sweets are limited. Olive oil is the primary source of fat in the Mediterranean diet, and moderate amounts of dairy products, such as cheese and yogurt, are also consumed.
The Mediterranean diet has numerous health benefits due to its nutrient-dense, whole-foods-based approach. It has been shown to reduce the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Try incorporating the top 10 foods mentioned in this article into your diet to transform your health.